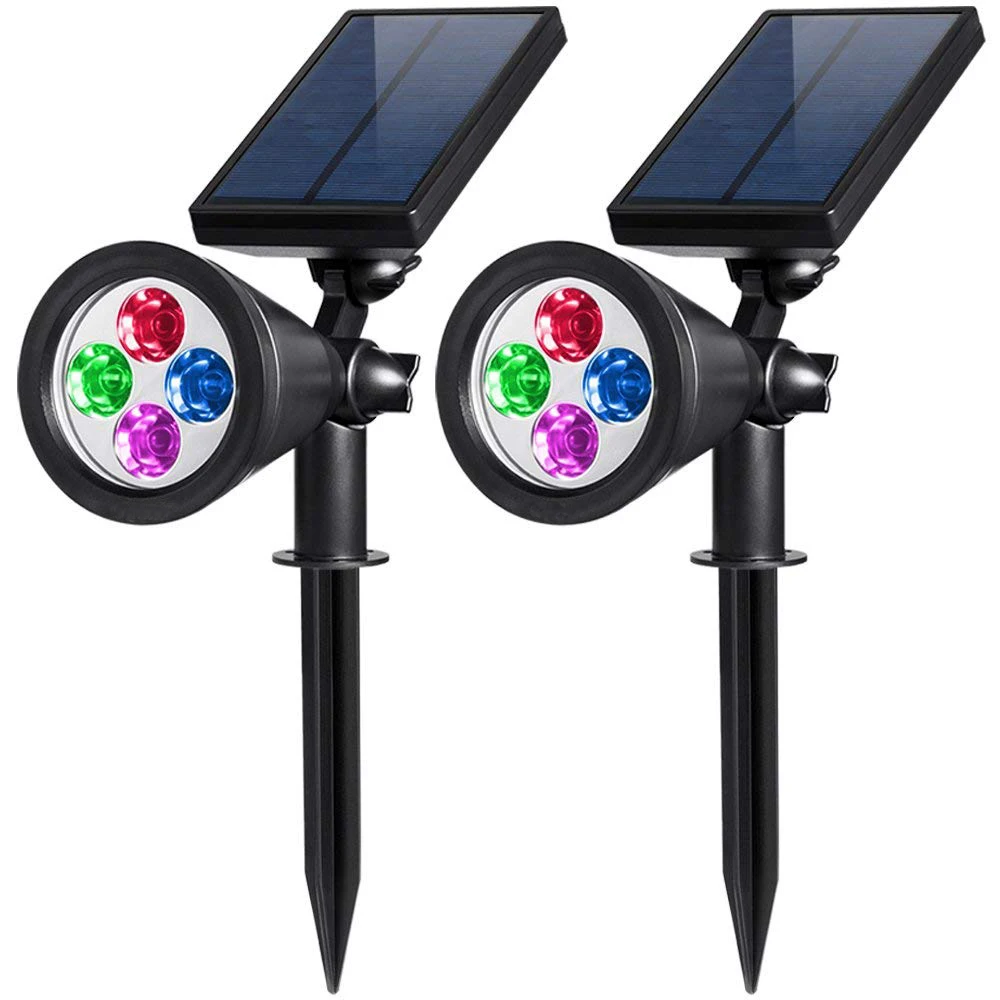
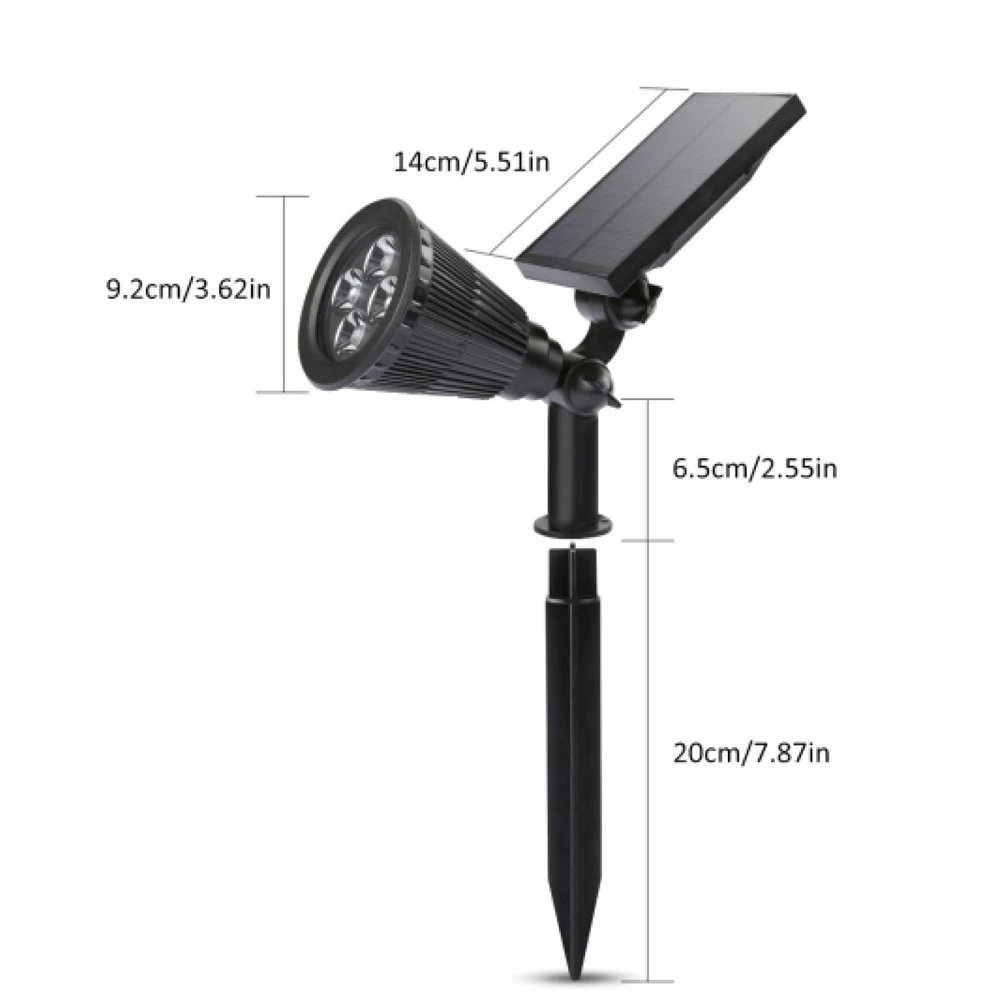
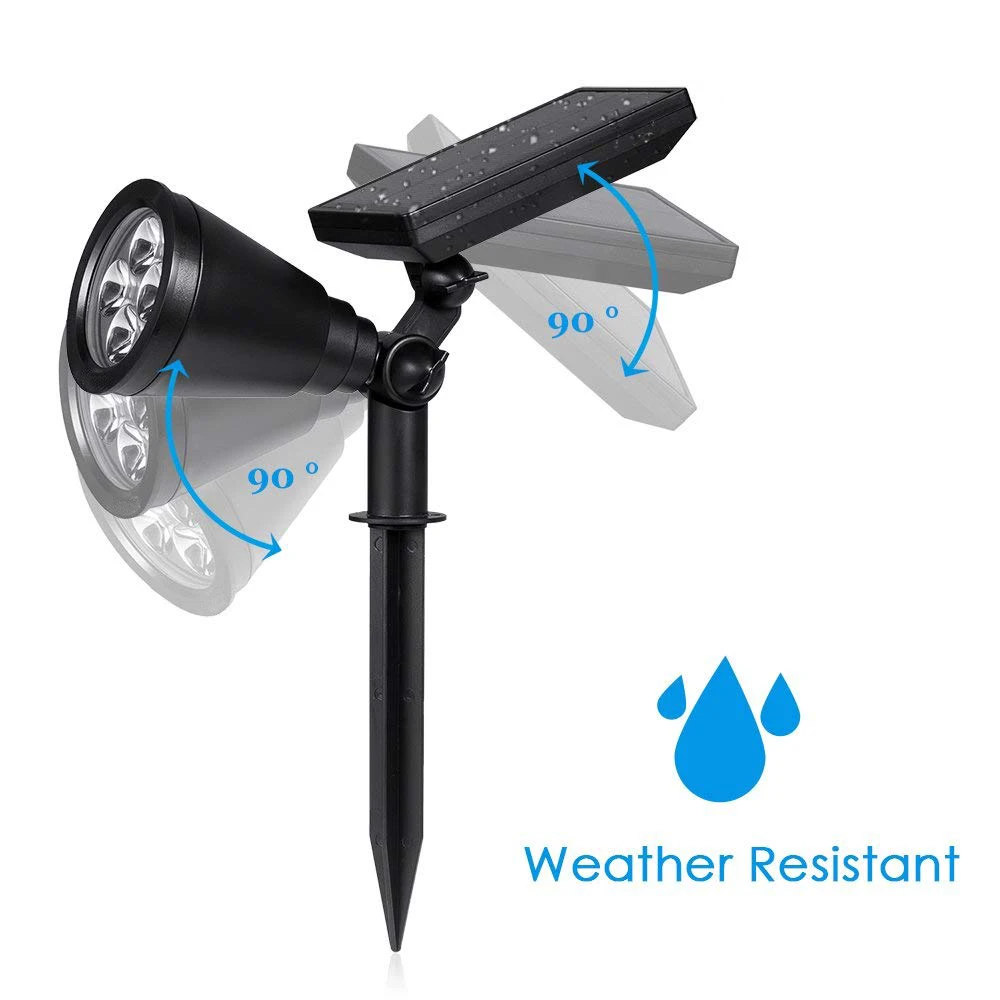
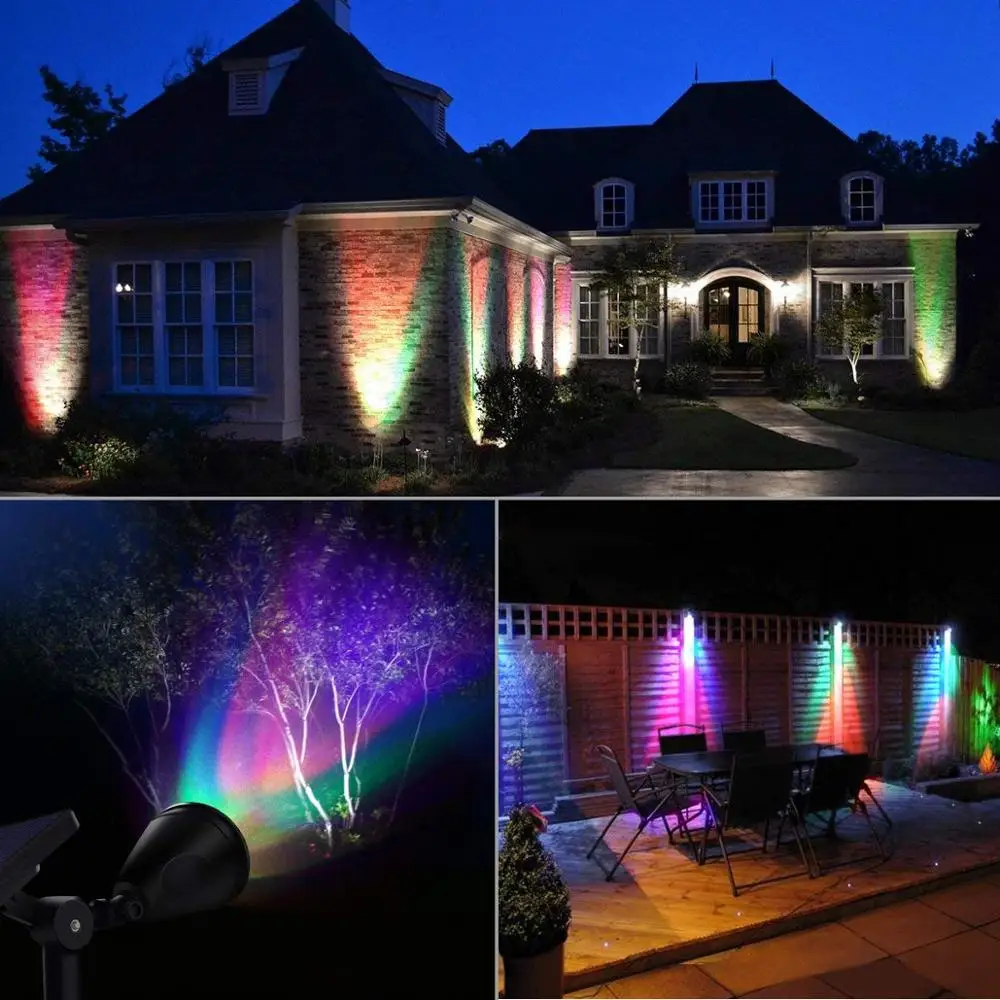
4 Luzes de Jardim LED RGB com Mudança Automática de Cor à Prova d'Água para Paisagismo Externo
- Visão Geral
- Produtos relacionados
Atividades de Marketing
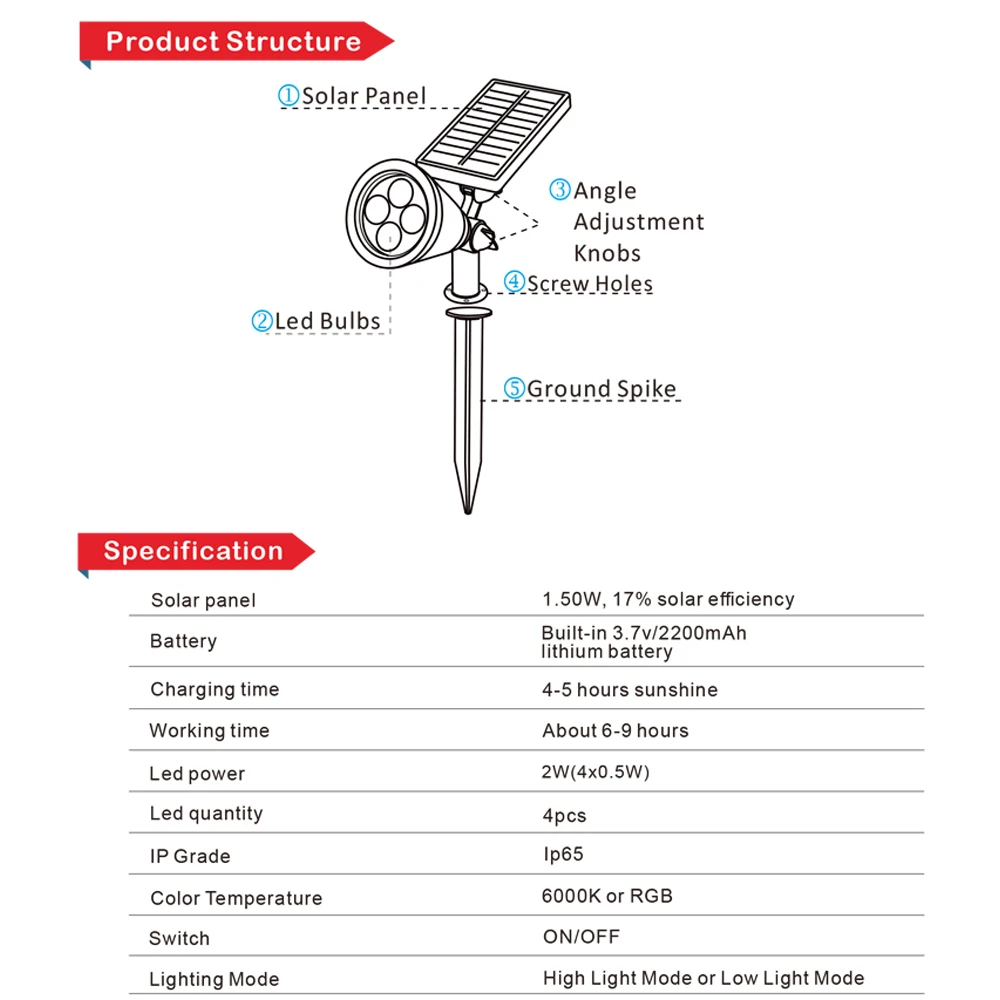
Descrição dos Produtos
Nome do Produto |
4 Luzes de Jardim LED RGB com Mudança Automática de Cor à Prova d'Água para Paisagismo Externo |








Perguntas frequentes
Q1: Quais são as condições de pagamento para novos clientes?
A: Normalmente, garantia comercial, opcional será cartão de crédito, visa, E-checking, western union ou T/T.
Q2: Qual é o prazo de entrega?
A: 3-5 dias para ordem de teste e 10-15 dias para a produção em massa.
Q3: Como você envia os produtos e quanto tempo leva para chegar?
A: Normalmente enviamos por DHL, UPS, FedEx ou TNT. Geralmente leva de 3 a 5 dias para chegar. Envio aéreo para a porta leva cerca de 15 dias.
Q4: Posso imprimir meu logo no suporte e na embalagem?
A: Sim, SEM MOQ para imprimir logo no suporte e na embalagem.
Q5. Alguma certificação para seus produtos?
-- CE, ROHS, PSE, Reach, UKCA etc, para que possam ser vendidos mundialmente com segurança!
Q6. Como proceder com um pedido de luz LED?
A: Primeiro, nos informe suas necessidades ou aplicação. Em segundo lugar, fornecemos orçamentos de acordo com seus requisitos ou nossas sugestões. Em terceiro lugar, o cliente confirma as amostras e faz um depósito para o pedido formal. Finalmente, organizamos a produção.
Q7: Como você envia os produtos e quanto tempo leva para chegar?
A: Pedidos pequenos seriam enviados por Expressos Internacionais (3-7 dias) ou pacote de logística internacional (15-20 dias). Pedidos em grande quantidade seriam enviados por via aérea (5-7 dias de aeroporto a aeroporto) e transporte marítimo (20-40 dias DDP)
Q8.Como você faz nosso negócio ter um relacionamento de longo prazo e bom?
-1.preço competitivo para fazer um ganha-ganha
-2.manter segredos para todos os nossos clientes cooperativos
-3.Enviar novas substituições com o próximo pedido para qualquer defeito.